Welcome to my personal website
I am an Earthquake Engineer
Here you can see my technical achievements and research activities
Biography-CV

- Personal Information:
Gender: Male
- Contact Information:
Email Address: v.shahmoradi@aut.ac.ir , vahidshahmoradi70@gmail.com
- Education:
Amirkabir University of Technology, Tehran, Iran
Thesis Topic: Seismic behavior of steel bridges with semi-active control method using fuzzy logic algorithm
Supervisor: Dr. Mohsen Tehranizadeh
Overall GPA: 3.53/4, 16.79/20
BSc., Civil Engineering 2010-2014
University of Zanjan, Zanjan, Iran
GPA:3.88/4, 18.03/20
High school diploma in Mathematics and Physics 2006-2010
Shahed high school, Zanjan, Iran
Overall GPA:17.52/20
- Research Interests
- Honors and Awards
- Ranked 3rd among 10 students of September,2014 Entrance of civil engineering of Amirkabir university of technology. 2016
- Ranked 1st among 36 students of September,2010 Entrance of civil engineering of university of Zanjan. 2014
- Ranked 12th in the “19th national Scientific and University Students Olympiad of Civil Engineering ”. Summer, 2014
- Ranked 3rd among the northwest student of Iran in the “19th national Scientific and University Students Olympiad of Civil Engineering ”. Spring 2014.
- Member of “Exceptional Talents of Amirkabir University of Technology”
- Member of “Exceptional Talents of University of Zanjan”
- Publications:
- Book:
- Shahmoradi.v. Book. Common English Phrase in ISI Papers. University of Zanjan, 2020,
- Paper
- Shahmoradi. V and Nasserasadi. K (2015), "Ranking some attenuation relationships and select an appropriate relationship for the Varzegan earthquake by LH and LLH tests", 10th international congress of civil engineering, Tabriz, Iran, Accepted.
- Shahmoradi. V and Nasserasadi. K (2015), "Define the competence magnitude and present an appropriate equations for convert Ms and Mb to Mw for Zanjan region", 2nd international congress on structure, architecture and urban development, Tabriz, Iran, Accepted. (verification Code: E-DEBKBGCEDJ). System Address: www.icsau.ir.
- Shahmoradi. V and Nasserasadi. K (2015), "Ranking some attenuation relationships and select an appropriate relationship for the Murmuri earthquake by LH and LLH tests", 2nd international congress on structure, architecture and urban development, Tabriz, Iran, Accepted. (verification Code: E-DECIJFCEDJ). System Address: www.icsau.ir.
- Shahmoradi. V and Nasserasadi. K (2014), "Ranking some attenuation relationships and select an appropriate relationship for the Kojur earthquake", 15th international congress on structure, architecture and urban development, Urmia, Iran, Accepted.
- Teaching Experience:
- Teaching Assistant for “Structural Analysis I”, Prof.NasserAsadi, Fall 2012. University of Zanjan, Zanjan , Iran. Responsible for holding problem sessions, providing solutions for problem sets, preparing lecture notes, grading.
- Teaching Assistant for “Structural Analysis I”, Prof.NasserAsadi, Fall 2014. University of Zanjan, Zanjan , Iran. Responsible for holding problem sessions, providing solutions for problem sets, preparing lecture notes, grading.
- Teaching Assistant for “Earthquake Engineering”, Prof.NasserAsadi, Fall 2016. University of Zanjan, Zanjan , Iran. Responsible for holding problem sessions, providing solutions for problem sets, preparing lecture notes, grading.
- Teaching Assistant for “Earthquake Engineering”, Prof.NasserAsadi, Fall 2017. University of Zanjan, Zanjan , Iran. Responsible for holding problem sessions, providing solutions for problem sets, preparing lecture notes, grading.
- Work Experience:
- Instructor of OpenSees workshop"Linear and non-linear modeling of 2D and 3D structures and different analysis in OpenSees"- Institute of science and technology- Qazvin- Iran- 2017
- Society and Committee Membership:
- Affiliate member of American Society of Civil Engineers. Member ID#: 10797204
- Member of Zanjan Construction Engineering. Member ID#: 30-3-0-05524
- Computer and Technical Skills
OpenSees, ETABS, SAP 2000, SAFE, Seismosignal, AutoCAD
General:
Microsoft Office (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, OneNote), MATLAB (Programming and GUI), Latex, EndNote, yEd, Mendely, Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Lightroom.
- Language skills:
- Persian: Native
- Turkish: Native
- English: Advanced.
- Arabic: Familiar- High-school knowledge in addition to the similarities with Persian.
- Software programmer
- Scale Master: A software which scales earthquake based on Iranian seismic code (2800). The software is scaling earthquake records without needing to another software like Seismosignal. This software can be use for both 2D and 3D structures. This software has been programmed in MATLAB and MATLAB GUI. Link: Go to software page
- Software for PSHA and DSHA Analysis: A software for Seismic hazard analysis that calculates PSHA and DSHA analysis. This program has been programmed by MATLAB GUI. Link: Go to software page
- Software for Liquefaction analysis based on ASCE and seed methods: A software for analyzing the liquefaction possibility in the one layer soil profiles under the earthquake excitation based on ASCE and Seed methods. This program has been programmed by MATLAB GUI. Link: Go to software page
- Selected Academic Courses:
- Dynamic of Structures: 17.5/20 - Prof. Mohsen Tehranizadeh
- Seismology and Earthquake Engineering:17/20 - Prof. Mohsen Tehranizadeh
- Soil Dynamics:17.75/20 - Dr. Mohammadreza Imam
- Advanced Steel Structures:17/20 - Dr. Abolghasem Keramati
- Thesis:19/20 - Prof. Mohsen Tehranizadeh
- Earthquake Engineering:18.5/20 Dr. Kiyarash Nasserasadi
- Structural Analysis I:18/20 Dr. Kiyarash Nasserasadi
- Structural Analysis II: 19.75/20 Dr. Kiyarash Nasserasadi
- Design of Steel Structures:19/20 Dr. Hosein Bayat
- Design of Concerete Structures: 18.5/20 Dr. Hosein Bayat
- Optimization of structures: 20/20 Dr. Mehdi Babaei
- Mechanic of Materials: 19/20 Dr. Massah
- Dynamic: 16.5/20 Dr. Sarang Seyrafiyan
- Mathematics I:17.75/20 Dr. Amiri
- Mathematics II:20/20 Dr. Saboori
- Physic: 19/20 Dr. Naemi
- Extracurricular activities and Hobbies:
- Sport: Swimming, Soccer
- Other: Reading book (Philosophy and Novels), Watching movie, Photography, Iranian Traditional and Pop Music
Scale Master software
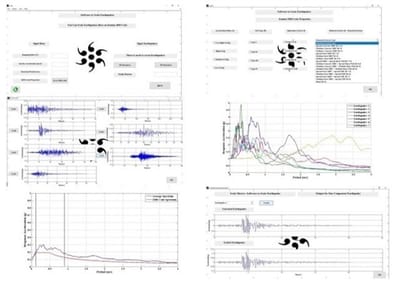
نرم افزار مورد نظر نرم افزار مقیاس زلزله ها بر اساس آیین نامه 2800 ایران می باشد که با استفاده از برنامه نویسی در نرم افزار متلب توسط اینجانب تولید گردیده است. نرم افزار قادر به مقیاس زلزله بریا سازه های دو بعدی و سه بعدی بوده و تمام مراحل مقیاس زلزله ها را به طور اتوماتیک و بدون نیاز به نرم افزار دیگر انجام می دهد.
Liquefaction software
Fuzzy logic system
Fuzzy logic was first proposed by Lotfi A. Zadeh of the University of California at Berkeley in a 1965 paper.[3] He elaborated on his ideas in a 1973 paper that introduced the concept of "linguistic variables", which in this article equates to a variable defined as a fuzzy set.[4] Other research followed, with the first industrial application, a cement kiln built in Denmark, coming on line in 1975. Fuzzy systems were initially implemented in Japan.
Fuzzy controllers are very simple conceptually. They consist of an input stage, a processing stage, and an output stage. The input stage maps sensor or other inputs, such as switches, thumbwheels, and so on, to the appropriate membership functions and truth values. The processing stage invokes each appropriate rule and generates a result for each, then combines the results of the rules. Finally, the output stage converts the combined result back into a specific control output value.
The most common shape of membership functions is triangular, although trapezoidal and bell curves are also used, but the shape is generally less important than the number of curves and their placement. From three to seven curves are generally appropriate to cover the required range of an input value, or the "universe of discourse" in fuzzy jargon.
As discussed earlier, the processing stage is based on a collection of logic rules in the form of IF-THEN statements, where the IF part is called the "antecedent" and the THEN part is called the "consequent". Typical fuzzy control systems have dozens of rules.
Consider a rule for a thermostat:
IF (temperature is "cold") THEN (heater is "high")
This rule uses the truth value of the "temperature" input, which is some truth value of "cold", to generate a result in the fuzzy set for the "heater" output, which is some value of "high". This result is used with the results of other rules to finally generate the crisp composite output. Obviously, the greater the truth value of "cold", the higher the truth value of "high", though this does not necessarily mean that the output itself will be set to "high" since this is only one rule among many. In some cases, the membership functions can be modified by "hedges" that are equivalent to adverbs. Common hedges include "about", "near", "close to", "approximately", "very", "slightly", "too", "extremely", and "somewhat". These operations may have precise definitions, though the definitions can vary considerably between different implementations. "Very", for one example, squares membership functions; since the membership values are always less than 1, this narrows the membership function. "Extremely" cubes the values to give greater narrowing, while "somewhat" broadens the function by taking the square root.
In practice, the fuzzy rule sets usually have several antecedents that are combined using fuzzy operators, such as AND, OR, and NOT, though again the definitions tend to vary: AND, in one popular definition, simply uses the minimum weight of all the antecedents, while OR uses the maximum value. There is also a NOT operator that subtracts a membership function from 1 to give the "complementary" function.
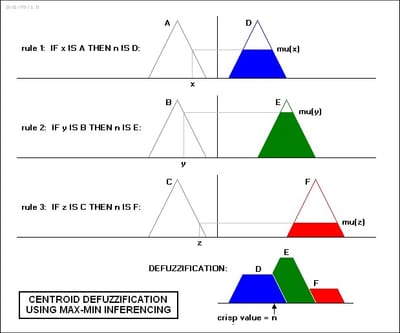
There are several ways to define the result of a rule, but one of the most common and simplest is the "max-min" inference method, in which the output membership function is given the truth value generated by the premise.
Rules can be solved in parallel in hardware, or sequentially in software. The results of all the rules that have fired are "defuzzified" to a crisp value by one of several methods. There are dozens, in theory, each with various advantages or drawbacks.
The "centroid" method is very popular, in which the "center of mass" of the result provides the crisp value. Another approach is the "height" method, which takes the value of the biggest contributor. The centroid method favors the rule with the output of greatest area, while the height method obviously favors the rule with the greatest output value.
The diagram below demonstrates max-min inferencing and centroid defuzzification for a system with input variables "x", "y", and "z" and an output variable "n". Note that "mu" is standard fuzzy-logic nomenclature for "truth value".
Source: wikipedia
About OpenSees

OpenSees, the Open System for Earthquake Engineering Simulation, is an object-oriented, software framework created at the NSF-sponsored Pacific Earthquake Engineering (PEER) Center. It allows users to create finite element applications for simulating the response of structural and geotechnical systems subjected to earthquakes. This framework was developed by Frank McKenna and Gregory L. Fenves with significant contributions from Michael H. Scott, Terje Haukaas, Armen Der Kiureghian, Remo M. de Souza, Filip C. Filippou, Silvia Mazzoni, and Boris Jeremic. OpenSees is primarily written in C++ and uses several Fortran numerical libraries for linear equation solving.
The license permits use, reproduction, modification, and distribution by educational, research, and non-profit entities for noncommercial purposes only. Use, reproduction and modification by other entities is allowed for internal purposes only. The UC Regents hold the copyright for OpenSees.
Users of OpenSees create applications by writing scripts in the Tcl programming language. The TclModelBuilder class in the OpenSees framework extends an instance of the Tcl interpreter with commands for finite element model building and analysis.
OpenSees developers access the source code using Apache Subversion. Although anyone may check-out the source code anonymously, only a handful of individuals have check-in access.
Source: Wikipedia
The logo is exclusive. designed by Vahid Shahmoradi
The license permits use, reproduction, modification, and distribution by educational, research, and non-profit entities for noncommercial purposes only. Use, reproduction and modification by other entities is allowed for internal purposes only. The UC Regents hold the copyright for OpenSees.
Users of OpenSees create applications by writing scripts in the Tcl programming language. The TclModelBuilder class in the OpenSees framework extends an instance of the Tcl interpreter with commands for finite element model building and analysis.
OpenSees developers access the source code using Apache Subversion. Although anyone may check-out the source code anonymously, only a handful of individuals have check-in access.
Source: Wikipedia
The logo is exclusive. designed by Vahid Shahmoradi









